An R-way Trie is a tree-like data structure, also known as a Prefix Tree or, more generically, a Digital Search Tree (DST)/Digital Tree. It is commonly used to implement string-based symbol-tables structures.
It has a certain resemblance to a binary-tree, but instead of having at most two children, each node can have multiple children (one for each character in the alphabet).
Structure
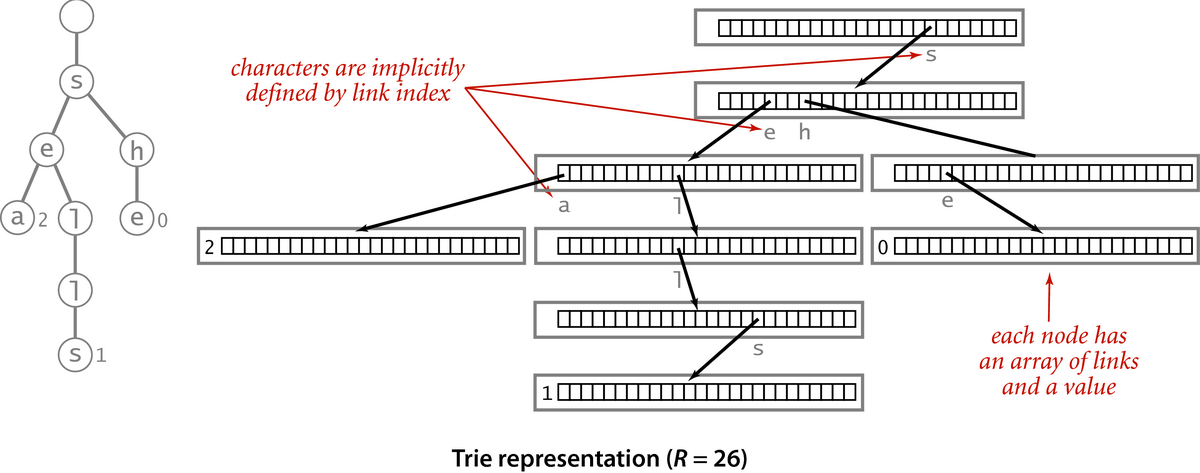
A trie consists of:
- Root node: Empty node that serves as the starting point
- Internal nodes: Each node represents a character
- Leaf nodes: Mark the end of a word
- Edges: Represent characters
Implementation
public class TrieNode
{
public Dictionary<char, TrieNode> Children { get; set; }
public bool IsEndOfWord { get; set; }
public TrieNode()
{
Children = new Dictionary<char, TrieNode>();
IsEndOfWord = false;
}
}
public class Trie
{
private readonly TrieNode _root;
public Trie()
{
_root = new TrieNode();
}
public void Insert(string word)
{
var node = _root;
foreach (char c in word)
{
if (!node.Children.ContainsKey(c))
{
node.Children[c] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node.Children[c];
}
node.IsEndOfWord = true;
}
public bool Search(string word)
{
var node = _root;
foreach (char c in word)
{
if (!node.Children.ContainsKey(c))
{
return false;
}
node = node.Children[c];
}
return node.IsEndOfWord;
}
public bool StartsWith(string prefix)
{
var node = _root;
foreach (char c in prefix)
{
if (!node.Children.ContainsKey(c))
{
return false;
}
node = node.Children[c];
}
return true;
}
}Operations
Insertion
Time Complexity: O(m) where m is the length of the word
public void Insert(string word)
{
var node = _root;
foreach (char c in word)
{
if (!node.Children.ContainsKey(c))
{
node.Children[c] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node.Children[c];
}
node.IsEndOfWord = true;
}Search
Time Complexity: O(m) where m is the length of the word
public bool Search(string word)
{
var node = _root;
foreach (char c in word)
{
if (!node.Children.ContainsKey(c))
{
return false;
}
node = node.Children[c];
}
return node.IsEndOfWord;
}Deletion
Time Complexity: O(m) where m is the length of the word
public void Delete(string word)
{
DeleteHelper(_root, word, 0);
}
private bool DeleteHelper(TrieNode node, string word, int index)
{
if (index == word.Length)
{
if (!node.IsEndOfWord)
{
return false;
}
node.IsEndOfWord = false;
return node.Children.Count == 0;
}
char c = word[index];
if (!node.Children.ContainsKey(c))
{
return false;
}
bool shouldDeleteChild = DeleteHelper(node.Children[c], word, index + 1);
if (shouldDeleteChild)
{
node.Children.Remove(c);
return node.Children.Count == 0;
}
return false;
}Applications
- Autocomplete: Suggest words as user types
- Spell Checker: Check if words exist in dictionary
- IP Routing: Longest prefix matching
- Text Analysis: Word frequency and pattern matching
Advantages
- Fast prefix searches: O(m) time complexity
- Space efficient: Shared prefixes save memory
- Predictable performance: No hash collisions
Disadvantages
- Memory usage: Can be high for sparse data
- Cache performance: Poor locality of reference
- Complexity: More complex than hash tables
Related Concepts
- binary-tree - Similar tree structure with different branching
- symbol-tables - Used for implementing symbol tables efficiently